Heroku This Website Is Temporarily Unavailable
What are some common bug that can exist detected with the handy router logs on Heroku? Nosotros'll explore them and show you how to address them easily and quickly with monitoring of Heroku from SolarWinds Papertrail.
One of the showtime cloud platforms, Heroku is a popular platform as a service (PaaS) that has been in evolution since June 2007. It allows developers and DevOps specialists to easily deploy, run, manage, and scale applications written in Scarlet, Node.js, Coffee, Python, Clojure, Scala, Become, and PHP.
To learn more near Heroku, head to the Heroku Architecture documentation.
Intro to Heroku Logs
Logging in Heroku is modular, similar to gathering system performance metrics. Logs are time-stamped events that can come from whatever of the processes running in all application containers (Dynos), arrangement components, or backing services. Log streams are aggregated and fed into the Logplex—a high-functioning, existent-time system for log delivery into a single channel.
Run-fourth dimension activity, as well as dyno restarts and relocations, can exist seen in the awarding logs. This will include logs generated from inside awarding code deployed on Heroku, services like the web server or the database, and the app's libraries. Scaling, load, and retention usage metrics, amidst other structural events, can exist monitored with system logs. Syslogs collect messages nigh actions taken by the Heroku platform infrastructure on behalf of your app. These are two of the most recurrent types of logs bachelor on Heroku.
To fetch logs from the command line, we can use the heroku logs command. More than details on this command, such every bit output format, filtering, or ordering logs, can exist found in the Logging commodity of Heroku Devcenter.
$ heroku logs 2019-09-16T15:13:46.677020+00:00 app[web.ane]: Processing PostController#list (for 208.39.138.12 at 2010-09-16 15:13:46) [Become] 2018-09-16T15:13:46.677902+00:00 app[web.1]: Rendering post/list 2018-09-16T15:13:46.698234+00:00 app[web.1]: Completed in 74ms (View: 31, DB: 40) | 200 OK [http://myapp.heroku.com/] 2018-09-16T15:13:46.723498+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=GET path='/posts' host=myapp.herokuapp.com' fwd='204.204.204.204' dyno=web.i connect=1ms service=18ms status=200 bytes=975 # © 2022 Salesforce.com. All rights reserved. Heroku Router Logs
Router logs are a special case of logs that exist somewhere between the app logs and the system logs—and are not fully documented on the Heroku website at the fourth dimension of writing. They carry information virtually HTTP routing within Heroku Mutual Runtime, which manages dynos isolated in a single multi-tenant network. Dynos in this network can simply receive connections from the routing layer. These routes are the entry and exit points of all web apps or services running on Heroku dynos.
Tail router only logs with the heroku logs -tp router CLI command.
$ heroku logs -tp router 2018-08-09T06:24:04.621068+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=GET path='/db' host=quiet-caverns-75347.herokuapp.com request_id=661528e0-621c-4b3e-8eef-74ca7b6c1713 fwd='104.163.156.140' dyno=web.ane connect=0ms service=17ms condition=301 bytes=462 protocol=https 2018-08-09T06:24:04.902528+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=GET path='/db/' host=tranquility-caverns-75347.herokuapp.com request_id=298914ca-d274-499b-98ed-e5db229899a8 fwd='104.163.156.140' dyno=web.1 connect=1ms service=211ms status=200 bytes=3196 protocol=https 2018-08-09T06:24:05.002308+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=GET path='/stylesheets/main.css' host=quiet-caverns-75347.herokuapp.com request_id=43fac3bb-12ea-4dee-b0b0-2344b58f00cf fwd='104.163.156.140' dyno=web.one connect=0ms service=3ms status=304 bytes=128 protocol=https 2018-08-09T08:37:32.444929+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=Become path='/' host=quiet-caverns-75347.herokuapp.com request_id=2bd88856-8448-46eb-a5a8-cb42d73f53e4 fwd='104.163.156.140' dyno=web.one connect=0ms service=127ms status=200 bytes=7010 protocol=https # Fig 1. Heroku router logs in the last Heroku routing logs always start with a timestamp and the "heroku[router]" source/component string, and and then a specially formatted message. This message begins with either "at=info", "at=alarm", or "at=error" (log levels), and can contain up to fourteen other detailed fields such as:
- Heroku error "code" (Optional) – For all errors and warning, and some info messages; Heroku-specific error codes that complement the HTTP status codes.
- Error "desc" (Optional) – Clarification of the error, paired to the codes to a higher place
- HTTP request "method" e.g. GET or POST – May be related to some issues
- HTTP asking "path" – URL location for the request; useful for knowing where to check on the application code
- HTTP request "host" – Host header value
- The Heroku HTTP Request ID – Can exist used to correlate router logs to application logs;
- HTTP asking "fwd" – X-Forwarded-For header value;
- Which "dyno" serviced the request – Useful for troubleshooting specific containers
- "Connect" time (ms) spent establishing a connexion to the web server(south)
- "Service" fourth dimension (ms) spent proxying data between the client and the web server(southward)
- HTTP response code or "status" – Quite informative in case of issues;
- Number of "bytes" transferred in total for this spider web request;
Common Problems Observed with Router Logs
Examples are manually colour-coded in this commodity. Typical ways to address the problems shown above are also provided for context.
Common HTTP Status Codes
404 Not Institute Error
Trouble: Fault accessing nonexistent paths (regardless of HTTP method):
2018-07-30T17:10:xviii.998146+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=POST path='/saycow' host=heroku-app-log.herokuapp.com request_id=e5634f81-ec54-4a30-9767-bc22365a2610 fwd='187.220.208.152' dyno=web.1 connect=0ms service=15ms condition=404 bytes=32757 protocol=https 2018-07-27T22:09:14.229118+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=GET path='/irobots.txt' host=heroku-app-log.herokuapp.com request_id=7a32a28b-a304-4ae3-9b1b-60ff28ac5547 fwd='187.220.208.152' dyno=web.1 connect=0ms service=31ms status=404 bytes=32769 protocol=https Solution: Implement or change those URL paths in the application or add the missing files.
500 Server Error
Problem: There's a bug in the application:
2018-07-31T16:56:25.885628+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info method=Become path='/' host=heroku-app-log.herokuapp.com request_id=9fb92021-6c91-4b14-9175-873bead194d9 fwd='187.220.247.218' dyno=web.1 connect=0ms service=3ms status=500 bytes=169 protocol=https Solution: The application logs have to be examined to determine the crusade of the internal error in the application'southward code. Note that HTTP Request IDs can exist used to correlate router logs against the web dyno logs for that same request.
Common Heroku Fault Codes
Other issues ordinarily detected by router logs can be explored in the Heroku Error Codes. Unlike HTTP codes, these mistake codes are not standard and only exist in the Heroku platform. They give more specific information on what may be producing HTTP errors.
H14 – No spider web dynos running
Trouble: App has no spider web dynos setup:
2018-07-30T18:34:46.027673+00:00 heroku[router]: at=error code=H14 desc='No spider web processes running' method=GET path='/' host=heroku-app-log.herokuapp.com request_id=b8aae23b-ff8b-40db-b2be-03464a59cf6a fwd='187.220.208.152' dyno= connect= service= status=503 bytes= protocol=https Notice that the above case is an actual error message, which includes both Heroku error code H14 and a description. HTTP 503 means "service currently unavailable."
Note that Heroku router error pages can be customized. These apply only to errors where the app doesn't reply to a request e.one thousand. 503.
Solution: Use the heroku ps:calibration command to outset the app's spider web server(s).
H12 – Request timeout
Problem: There's a request timeout (app takes more than 30 seconds to respond):
2018-08-18T07:11:15.487676+00:00 heroku[router]: at=fault lawmaking=H12 desc='Asking timeout' method=GET path='/slumber-thirty' host=serenity-caverns-75347.herokuapp.com request_id=1a301132-a876-42d4-b6c4-a71f4fe02d05 fwd='189.203.188.236' dyno=web.one connect=1ms service=30001ms condition=503 bytes=0 protocol=https Error code H12 indicates the app took over 30 seconds to respond to the Heroku router.
Solution: Code that requires more than 30 seconds must run asynchronously (eastward.g., as a groundwork chore) in Heroku. For more info read Request Timeout in the Heroku DevCenter.
H18 – Server Request Interrupted
Trouble: The Application encountered as well many requests (server overload):
2018-07-31T18:52:54.071892+00:00 heroku[router]: sock=backend at=fault code=H18 desc='Server Request Interrupted' method=GET path='/' host=heroku-app-log.herokuapp.com request_id=3a38b360-b9e6-4df4-a764-ef7a2ea59420 fwd='187.220.247.218' dyno=web.ane connect=0ms service=3090ms status=503 bytes= protocol=https Solution: This trouble may indicate that the application needs to be scaled up, or the app functioning improved.
H80 – Maintenance style
Problem: Maintenance mode generates an info router log with error lawmaking H18:
2018-07-30T19:07:09.539996+00:00 heroku[router]: at=info code=H80 desc='Maintenance mode' method=Get path='/' host=heroku-app-log.herokuapp.com request_id=1b126dca-1192-4e98-a70f-78317f0d6ad0 fwd='187.220.208.152' dyno= connect= service= status=503 bytes= protocol=https Solution: Disable maintenance mode with heroku maintenance:off
Papertrail
Papertrail™ is a cloud log management service designed to aggregate Heroku app logs, text log files, and syslogs, amongst many others, in one place. It helps you to monitor, tail, and search logs via a spider web browser, command-line, or an API. The Papertrail software analyzes log letters to observe trends, and allows you to react instantly with automated alerts.
The Event Viewer is a alive aggregated log tail with motorcar-scroll, suspension, search, and other unique features. Everything in log messages is searchable, and new logs still stream in real time in the outcome viewer when searched (or otherwise filtered). Notation that Papertrail reformats the timestamp and source in its Event Viewer to make information technology easier to read.
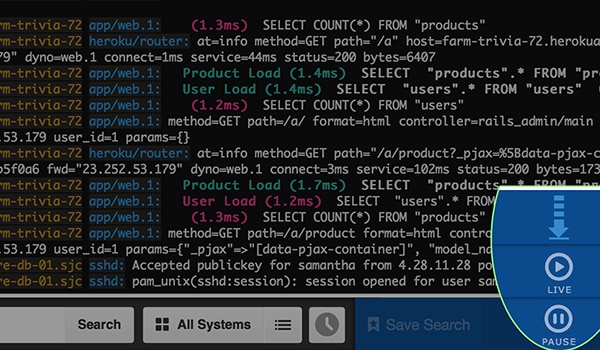 Fig 2. The Papertrail Issue Viewer. © 2022 Solarwinds. All rights reserved.
Fig 2. The Papertrail Issue Viewer. © 2022 Solarwinds. All rights reserved.
Provisioning Papertrail on your Heroku apps is extremely easy: heroku addons:create papertrail from terminal. (See the Papertrail article in Heroku'southward DevCenter for more info.) Once setup, the add-on can be open from the Heroku app's dashboard (Resources section) or with heroku addons:open papertrail in terminal.
Troubleshooting Routing Problems Using Papertrail
A bully way to examine Heroku router logs is by using the Papertrail solution. Information technology'south easy to isolate them in order to filter out all the dissonance from multiple log sources: but click on the "heroku/router" program name in whatsoever log message, which will automatically search for "programme:heroku/router" in the Event Viewer:
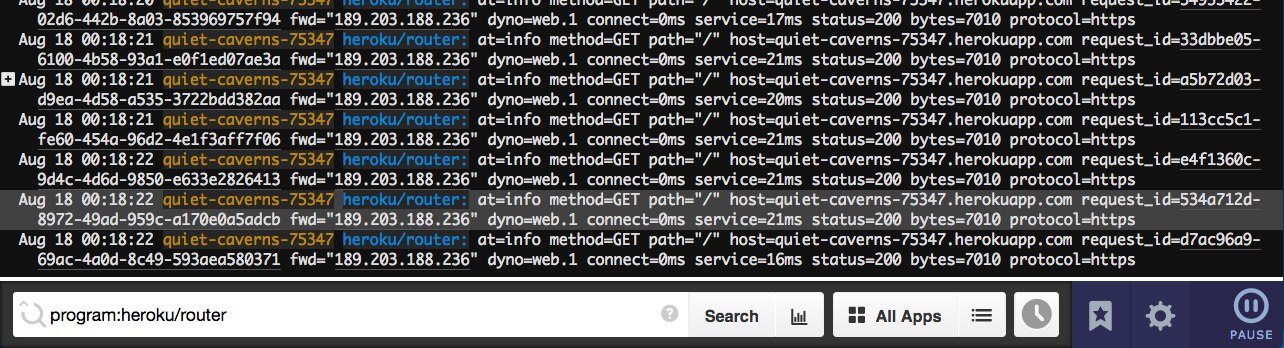
Fig iii. Tail of Heroku router logs in Papertrail, 500 app error selected. © 2022 SolarWinds. All rights reserved.
Monitor HTTP 404s
How do y'all know that your users are finding your content, and that it's up to date? 404 Non Found errors are what a client receives when the URL'southward path is non found. Examples would be a misspelled file name or a missing app road. Nosotros want to make sure these types of errors remain uncommon, because otherwise, users are either walking to expressionless ends or seeing irrelevant content in the app!
With Papertrail, setting upward an alarm to monitor the amount of 404s returned by your app is like shooting fish in a barrel and convenient. Ane way to do it is to search for "status=404" in the Event Viewer, and so click on the Save Search button. This will bring up the Salve Search popup, forth with the Save & Setup Warning option:
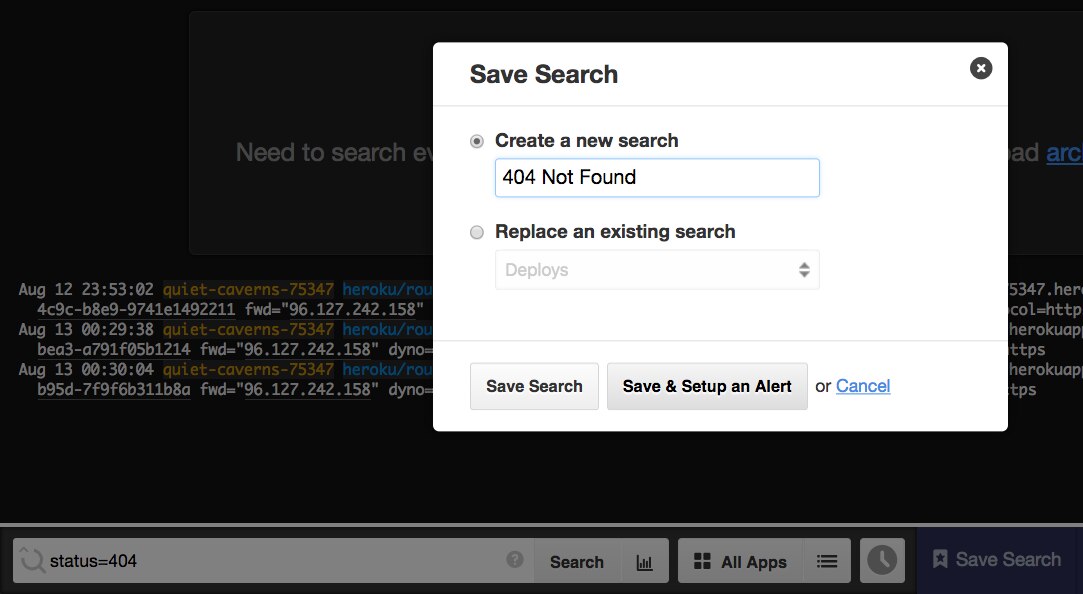
Fig 4. Save a log search and ready an alert with a unmarried action © 2022 SolarWinds. All rights reserved.
The following screen will give us the alert commitment options, such every bit email, Slack message, push button notifications, or even publish all matching events as a custom metric for application functioning management tools such as AppOptics™.
Troubleshoot 500 errors quickly
Fig five. HTTP 500 Internal Server Error from herokuapp.com. © 2022 Google LLC. All rights reserved.
Permit'south say an HTTP 500 error is happening on your app after it's deployed. A great characteristic of Papertrail is to brand the request_id in log messages clickable. Simply click on it or copy it and search it in the Issue Viewer to find all the app logs that are causing the internal problem, forth with the detailed mistake message from your awarding's code.
Determination
Heroku router logs are the mucilage between web traffic and (sometimes intangible) errors in your application code. It makes sense to give them special focus when monitoring a wide range of issues because they often bespeak client-facing problems that we want to avert or address ASAP. Add the Papertrail addon to Heroku to go more than powerful ways to monitor router logs.
Sign up for a 30-day gratis trial of Papertrail and beginning aggregating logs from all your Heroku apps and other sources. You lot may learn more about the Papertrail advanced features in its Heroku Dev Eye article.
Source: https://www.papertrail.com/blog/analyzing-heroku-router-logs-with-papertrail/
Post a Comment for "Heroku This Website Is Temporarily Unavailable"